Archaeology is built on physical evidence, yet some discoveries initially appeared so improbable they were dismissed as errors or exaggerations. Over time, careful excavation, laboratory testing, and peer-reviewed research confirmed that these finds were genuine. Together, these 10 Archaeology Discoveries demonstrate that ancient societies were often more technologically skilled, socially complex, and intellectually capable than previously assumed.
Table of Contents
10 Archaeology Discoveries
| Key Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Oldest known mechanical device | Antikythera Mechanism dated to ~100 BCE |
| Earliest symbolic Neanderthal behavior | Animal skull ritual site ~43,000 years old |
| Prehistoric mathematics | Ishango Bone shows intentional numeric patterning |
| Surgery before modern medicine | Evidence of trepanation with survival rates |
| Stone tools older than Homo sapiens | Tools dated to 3.3 million years ago |
Why These Discoveries Matter
For decades, archaeology textbooks portrayed early humans as technologically limited and culturally simplistic. That narrative has steadily eroded as discoveries accumulated across Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
“Each of these finds forces us to rethink what we mean by ‘advanced,’” said Dr. Brian Fagan, emeritus professor of anthropology at the University of California, Santa Barbara. “Human innovation did not follow a straight line. It emerged in bursts, often much earlier than expected.”
The 10 Archaeology Discoveries discussed here are not curiosities. They are evidence-based challenges to assumptions about intelligence, planning, symbolic thought, and engineering in the ancient world.
The Science Behind Verification
Before entering the academic record, major archaeological claims undergo extensive scrutiny. Methods commonly used include:
- Radiocarbon and uranium-series dating
- Microscopic wear analysis
- CT scans and X-ray tomography
- Isotope and metallurgical testing
- Stratigraphic verification by independent teams
According to the Society for American Archaeology, replication and cross-disciplinary review are critical in distinguishing authentic discoveries from misinterpretation.
The Discoveries
1. The Antikythera Mechanism: An Ancient Computer
Recovered from a Greek shipwreck in 1901, the Antikythera Mechanism baffled researchers for decades. Advances in imaging later revealed a system of interlocking bronze gears designed to predict eclipses, planetary motion, and lunar cycles.
A peer-reviewed reconstruction published in Nature concluded the device functioned as an analog computer, built more than 1,000 years before similar mechanical systems appeared in Europe.
“This was not an isolated experiment,” said Dr. Alexander Jones, historian of ancient science at New York University. “It reflects a sophisticated tradition of mechanical knowledge.”
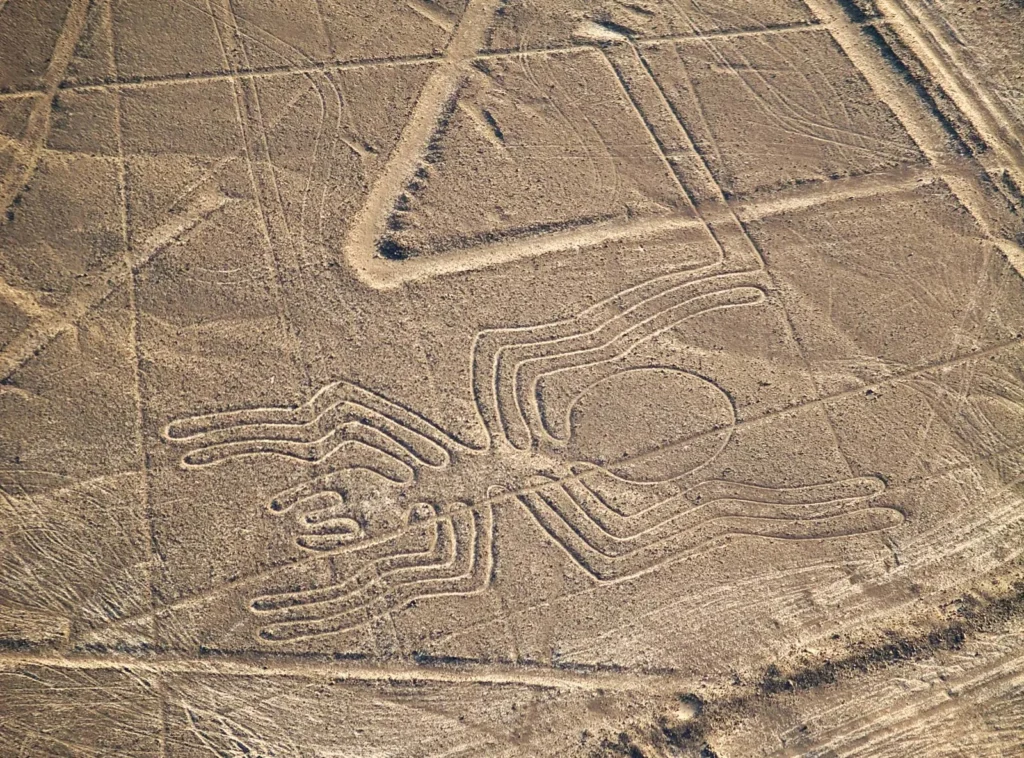
2. The Nazca Lines: Engineering Without Flight
Spanning hundreds of square kilometers in southern Peru, the Nazca Lines depict animals, plants, and abstract shapes etched into desert soil between 500 BCE and 500 CE.
Archaeologists confirmed the geoglyphs were created using rope grids and ground-based surveying. Their scale suggests coordinated labor and long-term planning rather than spontaneous creation.

3. The Stone Spheres of Costa Rica
More than 300 near-perfect stone spheres were shaped from hard igneous rock by the Diquís culture. Some measure over two meters in diameter and weigh up to 15 tons.
Despite speculation, researchers from Costa Rica’s National Museum confirmed they were deliberately crafted using abrasion techniques. Their alignment patterns suggest social or political symbolism.
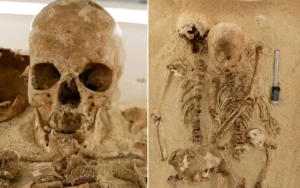
4. Neanderthal Ritual Behavior
Excavations at Des-Cubierta Cave in Spain revealed deliberately placed skulls of large mammals. Dating confirms Neanderthals collected and arranged these remains over centuries.
The findings challenge the outdated view that Neanderthals lacked symbolic thought. According to Science Advances, the behavior likely carried cultural meaning.
5. The Ishango Bone and Prehistoric Mathematics
Discovered near the Congo-Uganda border, the Ishango Bone contains carefully grouped notches dated to roughly 20,000 years ago. Some scholars interpret the markings as arithmetic sequences or lunar tracking.
While interpretations vary, consensus holds the markings were intentional and meaningful.
Discoveries That Changed Assumptions About Technology
6. Meteorite Iron Tools
Chemical signatures show that some ancient tools were forged from meteoritic iron long before humans mastered smelting. This includes artifacts from Egypt and Central Europe.
The discovery demonstrates early experimentation with rare materials, not technological ignorance.
7. Bog Bodies and Natural Preservation
In Northern Europe, acidic peat bogs preserved human remains with skin, hair, and facial features intact for thousands of years.
Forensic analysis reveals cause of death, diet, and even last meals, offering unparalleled insight into Iron Age societies.
8. Underground Cities of Anatolia
Sites such as Derinkuyu in modern Turkey extend multiple levels underground and include ventilation systems, wells, and communal spaces.
Archaeologists believe they served as long-term refuges rather than temporary shelters, indicating advanced urban planning.
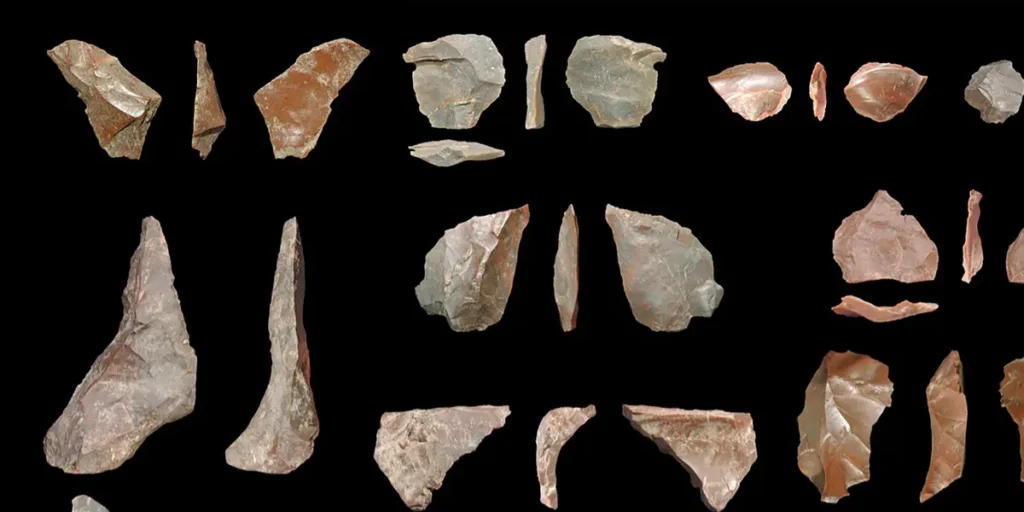
9. Stone Tools Older Than Homo sapiens
In 2015, researchers announced the discovery of stone tools in Kenya dated to 3.3 million years ago, predating Homo sapiens by more than a million years.
The find suggests tool-making began with earlier hominin species, redefining cognitive evolution timelines.
10. Prehistoric Brain Surgery
Trepanation—drilling holes into the skull—has been documented across continents. Many skulls show signs of healing, proving patients survived.
According to medical historians writing in The Lancet, this represents early surgical knowledge rather than superstition.
What These Discoveries Reveal Collectively
Taken together, these 10 Archaeology Discoveries demonstrate that innovation, symbolism, and problem-solving are deeply rooted in human ancestry.
“Complex behavior didn’t suddenly appear,” said Dr. Sarah Parcak, archaeologist and space archaeology pioneer. “It accumulated across cultures in ways we’re only beginning to recognize.”
Ongoing Debates and Open Questions
Not all interpretations are settled. Scholars continue to debate:
- The symbolic meaning of stone spheres
- Whether Ishango Bone markings represent arithmetic or calendars
- The social function of underground cities
Disagreement, researchers emphasize, is a strength of archaeology, not a weakness.
Looking Ahead
New tools such as artificial intelligence, satellite imaging, and non-invasive scanning are accelerating discoveries worldwide. Archaeologists say future findings may further challenge modern assumptions about the ancient past.
As Parcak noted, “What seems unbelievable today often becomes tomorrow’s textbook fact.”
FAQ
Are these discoveries universally accepted?
The physical evidence is verified. Interpretations may differ, but authenticity is not in doubt.
Why did these discoveries seem fake at first?
They conflicted with older assumptions about early human capability.
Do these findings rewrite history?
They refine and expand history rather than overturning it.